What Is Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP)?
A cloud workload is an atomic unit of cloud functionality, consisting of all components required to run it, such as data and network connectivity. Here are several examples of cloud workloads:
- An API—serving as part of a customer-facing application.
- A computing component handling back-end processing.
- The front end of an internal business application.
- A virtual machine (VM) running in the cloud.
- A containerized application consisting of an application and the supporting middleware that runs in a container engine like Docker or an orchestrator like Kubernetes.
A CWPP provides a mechanism that protects cloud workloads consistently across multiple cloud environments and complex architectures. For example, a CWPP can protect a hybrid cloud by providing capabilities that let you apply the same security properties and risk reduction value across all environments. With cloud-native applications, workload security must start proactively during development as well as protecting workloads dynamically at runtime, supporting a DevSecOps organizational model.
In this article:
- Why are Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) Needed?
- Security Benefits of CWPP
- Securing Virtualized, Container, and Serverless Environments
- Consistency Across Cloud Environments
- Secure Portability of Workloads
- How Does CWPP Work? [P2]
- CWPP and CSPM
- CWPP Implementation Tips
- Aqua Security Cloud Workload Protection Platform
Why are Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) Needed?
Here are four reasons why a Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) is essential:
- Organizations have legacy infrastructure and applications—these legacy infrastructures make it difficult to move all functionality to the cloud.
- Organizations use multiple cloud providers—many organizations are using several cloud vendors and working in a multi-cloud, hybrid environment. This approach makes it hard for security personnel to see, know and control where applications and data are within this irregular environment.
- Tradeoff of development velocity for security—rapid development of applications in a CI/CD pipeline often means that security is no longer a stringent gate for applications and workloads. Security experts can’t initiate controls at application run time like they could in the past.
Applications and data are at risk because of the lack of visibility and control, the changing nature of workloads, and the prevalence of the DevOps environment. CWPP can address these challenges because it is built for a multi-cloud environment and is able to assess and secure workloads at runtime.
Related content: Read our guide to secure software development lifecycle ›
Security Benefits of CWPP
Here are key advantages of a CWPP to a modern organization running workloads in the cloud.
Securing Virtualized, Container, and Serverless Environments
Legacy security tools run on a physical server or managed endpoints. These tools were not designed without containers, virtualization, serverless functions, or platform as a service (PaaS) in mind. Modern workload protection must span virtual machines, containers and serverless workloads in public and private clouds.
Consistency Across Cloud Environments
Unless an organization takes preventative action, the following factors can reduce the visibility of cloud workloads:
- The microservices architecture creates a larger number of smaller workloads.
- DevOps has caused a decrease in the lifespan of each workload, as workloads are destroyed and replaced with newer versions to keep up with the pace of development.
- Many organizations use hybrid cloud and multi-cloud.
CWPPs offer organizations consistent visibility into their workloads, even if they work with numerous workloads in multiple locations, both on-premises and in the cloud.
Secure Portability of Workloads
CWPP makes it possible to move workloads between environments without compromising security. For example, without CWPP if a virtual machine (VM) is running in an on-premises VMware data center and is then migrated to a container running in a public cloud, security needs to be configured from scratch because the infrastructure is completely different. With CWPP, it is still the same workload secured continuously before and after migration.
Related content: Read our guide to application security in the cloud ›
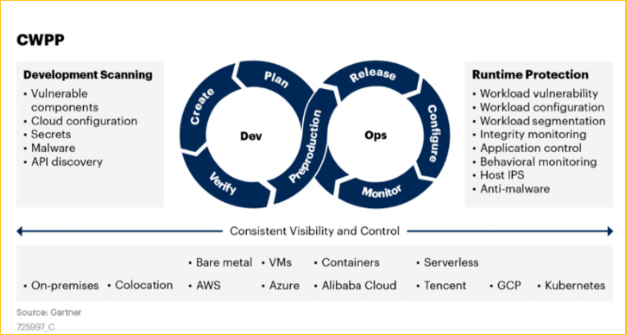
How Does CWPP Work?
A CWPP protects server workloads by providing visibility into all server workloads across all locations, alongside specialized security controls. Here is how CWPPs typically work to protect your cloud workloads:
- Protection at runtime – CWPPs use several features to protect your cloud workloads. Notable features include system integrity protection, behavioral monitoring, application control, anti-malware protection, and host-based intrusion prevention.
- Scanning and remediation – a CWPP scans for known vulnerabilities and risks and then provides remediation options. For example, the solution may implement or recommend security patches to fix the detected issues. It typically involves using techniques like integrity protection and allowlists.
- Protecting against common threats – CWPPs can protect against common security threats affecting both on-premises and cloud workloads. It usually involves implementing network segmentation, malware detection and remediation, and runtime protection.
CWPP and CSPM
Both CWPP and CSPM solutions aim to address cloud security but offer a different value. CWPP solutions aim to provide targeted protection for on-premises and cloud workloads.
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions aim to address issues related to cloud security misconfigurations. These solutions scan your cloud environments for issues such as:
- Misconfigured security settings.
- Configurations that violate corporate security policies.
- Configurations that violate regulatory compliance requirements.
CSPMs are a key component of CWPP because ensuring correct configuration is critical for application security.
CWPP Implementation Tips
To implement a successful CWPP program, Gartner provides the following tips for risk and security management leaders:
- Design for control and visibility of workloads regardless of size or location.
- Replace conventional access strategies with a zero trust “deny all by default” attitude to workload protection.
- Make it a prerequisite that CWPP tools expose functionality via APIs.
- Apply workload compliance as an integral part of the CI/CD cycle, including security scanning for container images, serverless functions, and infrastructure as code (IaC) templates.
- Find a solution for situations where CWPP agents cannot be used.
Aqua Security Cloud Workload Protection Platform
When it comes to workload protection at runtime – prevention and detection isn’t enough. Runtime security means stopping attacks in progress. Aqua Security’s runtime protection, detection, and response capabilities can protect all of your workloads, across clouds and platforms.
